NEWS FEED

Delaware Tourism Office Announces Latest Round of Sports Tourism Capital Investment Fund Awardees
Date Posted: December 20, 2024

Scuse Has Always Hung His Hat Up In Delaware
Date Posted: December 20, 2024

Recycle Holiday Trees in the New Year at Delaware Center for Horticulture’s TreeCycle Event Jan. 4
Date Posted: December 20, 2024

Governor Carney, DNREC, Seaford Celebrate Investments in Riverfront Redevelopment
Date Posted: December 19, 2024

Office of the Marijuana Commissioner (OMC) Conducts Lottery for Open Retail Licensing
Date Posted: December 19, 2024

Delaware’s ABLE Program Receives Funding from DHSS
Date Posted: December 19, 2024

DNREC Releases Updated State Energy Plan
Date Posted: December 19, 2024

Governor Carney Issues Statement on Senate Confirmations
Date Posted: December 16, 2024

Holiday Safety
Date Posted: December 16, 2024

Statement from Governor Carney
Date Posted: December 14, 2024

2024 Electoral College
Date Posted: December 13, 2024

Presidential Daughter Ashley Biden, Gov. Carney, DNREC Secretary Garvin Rededicate Renovated Biden Environmental Center
Date Posted: December 13, 2024

Delaware Natural Resources Police, DNREC Again Stock Santa’s Sleigh Via USMC Reserve Toys for Tots Partnership
Date Posted: December 13, 2024

Office of the Marijuana Commissioner (OMC) Open Retail License Lottery
Date Posted: December 13, 2024

Rooted in Tradition: 160 Delaware Farms Celebrate Over 100 Years
Date Posted: December 12, 2024

Governor Carney Announces Leadership Change at the Department of Transportation
Date Posted: December 12, 2024

$1.45 Million in Grants Announced to Support Homeless Services in Delaware
Date Posted: December 12, 2024

Governor Carney Announces Next Steps to Expand Access to High-Speed Broadband
Date Posted: December 11, 2024

Newly Released Federal Report Highlights Complexity of PFAS Exposure
Date Posted: December 10, 2024

Millsboro Fire
Date Posted: December 10, 2024

AG Jennings announces more than 135 charges in indictment against Wilmington-area gang
Date Posted: December 10, 2024
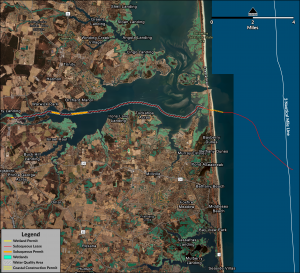
DNREC Approves Permits for US Wind Offshore Project
Date Posted: December 9, 2024

Delaware Paramedics Administer 250th Unit of Whole Blood for Prehospital Care
Date Posted: December 9, 2024

Laurel Fire
Date Posted: December 9, 2024

Delaware Day Adventure Begins December 7
Date Posted: December 6, 2024

E-ZPass Delaware Announces Annual Free Transponder Event
Date Posted: December 5, 2024

DSHA Celebrates Home Sweet Home For The Holidays Program And $75 Million In Additional Assistance
Date Posted: December 5, 2024

Cheswold Fire
Date Posted: December 4, 2024

Frederica Fire
Date Posted: December 4, 2024

AG Jennings reaches agreement with recidivist Wilmington landlord to shut down operations in Delaware
Date Posted: December 4, 2024

Delaware Office of Highway Safety Encourages Safe Driving Decisions for Seniors and Their Loved Ones
Date Posted: December 3, 2024

Nominations Open for 2025 Governor’s Volunteer Service Awards
Date Posted: December 3, 2024

Smyrna administrative assistant named 2025 Delaware Educational Support Professional of the Year
Date Posted: December 2, 2024

Delaware 250 Announces Fall 2024 Grant Recipients
Date Posted: December 2, 2024

The Mezzanine Gallery to Exhibit Lori Crawford’s “EnvironMental Just(ice) Mercy”
Date Posted: December 2, 2024

Winter Weather Awareness Week: December 2 to 6
Date Posted: November 27, 2024

2025 Delaware State Parks Annual Passes, Surf Fishing Permits to Go on Sale Dec. 3
Date Posted: November 27, 2024

DHSS Adds New Data and Reports to the CostAware Website
Date Posted: November 26, 2024

Delaware Celebrates National Adoption Month
Date Posted: November 26, 2024

Thanksgiving Safety 2024
Date Posted: November 26, 2024

DNREC Begins Emergency Dredging Project Restoring Beach North of Indian River Inlet
Date Posted: November 25, 2024

Burn Ban Lifted
Date Posted: November 25, 2024

Registration Open for 2025 Junior Solar Sprint
Date Posted: November 25, 2024

Celebrate the Holidays in Delaware with the Hidden Holiday Gems Passport
Date Posted: November 22, 2024

Governor Carney Proclaims November 17-23 as Delaware Apprenticeship Week
Date Posted: November 22, 2024

Governor Carney Announces Judicial Nominations
Date Posted: November 22, 2024

Delaware Office of Highway Safety Launches Sober Rides Initiative and Kicks Off Winter Holiday Road Safety Campaign
Date Posted: November 21, 2024

Governor Carney, DSB Announce Fall 2024 EDGE Grant Competition Awards
Date Posted: November 20, 2024

City Of Wilmington Celebrates Ten Years Of Downtown Development Districts
Date Posted: November 20, 2024

Division of Revenue Releases Guidance on New Short-term Rental Lodging Tax
Date Posted: November 20, 2024

DOJ secures life plus decades more in prison for domestic violence repeat offender
Date Posted: November 19, 2024

Federal Court Orders Harris Jewelry to Restore its Website and Portal for Servicemembers to Request Refunds
Date Posted: November 19, 2024

Agriculture, Food and Natural Science Students Take Home Awards from 97th National FFA Convention & Expo
Date Posted: November 19, 2024

Delaware Forest Service To Host Upcoming Wildfire Training
Date Posted: November 18, 2024

Delaware’s Sports Tourism Industry Contributed Significant Economic Impact in 2023, According to Recent Study
Date Posted: November 15, 2024

Delaware Celebrates Improvements To The Housing Assistance Application Process
Date Posted: November 15, 2024

Delaware Natural Resources Police Collecting Toys for Tots Donations for Kids
Date Posted: November 15, 2024

Delaware State Housing Authority Recognizes Mortgage Lending Community And Veterans At 2024 Annual Lender Meeting
Date Posted: November 14, 2024

Delaware Officials Unveil Harm Reduction Vending Machines
Date Posted: November 14, 2024

2025 District/Charter Educational Support Professionals of the Year Honored
Date Posted: November 14, 2024

Historical Marker Dedicated – Mount Olive Holiness Pentecostal Church in Smyrna
Date Posted: November 13, 2024

DelDOT Receives Top Bond Rating and Announces Bond Sale
Date Posted: November 12, 2024

Delaware’s Education Savings Plan Earns Silver Rating
Date Posted: November 7, 2024

Delaware Schools Receive National, State Honors
Date Posted: November 6, 2024

DNREC to Host Nov. 14 Webinar about Storm Water Management and Living Shorelines
Date Posted: November 6, 2024

Governor Carney Releases Government Efficiency and Accountability Review (GEAR) Board Report
Date Posted: November 4, 2024

DOJ secures conviction in the killing of Cynthia Amalfitano
Date Posted: November 4, 2024

AG Jennings and bipartisan coalition of 30 states announce finalization of settlement with Kroger over opioid crisis
Date Posted: November 4, 2024

Carney Administration Outlines Investments in Electric Vehicle Infrastructure
Date Posted: November 1, 2024

Open Enrollment on Delaware’s Health Insurance Marketplace Starts Nov. 1
Date Posted: November 1, 2024

AG Jennings Announces Cooperation Agreements and Settlements with Heritage and Apotex totaling $49.1 Million
Date Posted: November 1, 2024

DNREC Reopens Castle Trail Along C&D Canal Following Repairs to Storm-Damaged Section
Date Posted: October 31, 2024

Delaware Partners with American Cancer Society for 2nd Annual Lung Cancer Screening Campaign
Date Posted: October 31, 2024

OMC Provides Update on License Lottery and Selected Applicants for Delaware’s Marijuana Industry
Date Posted: October 31, 2024

Funding Awarded for Tree-Planting Projects
Date Posted: October 31, 2024

With Annual Fall Trout Stocking in White Clay Creek, DNREC Delivers Angling Opportunities
Date Posted: October 30, 2024

Carney, Carper, Coons, Blunt Rochester Announce Over $127 Million in Federal Funding to Decarbonize Port Wilmington
Date Posted: October 30, 2024

Governor Carney Launches Statewide Student Mentoring Program
Date Posted: October 29, 2024
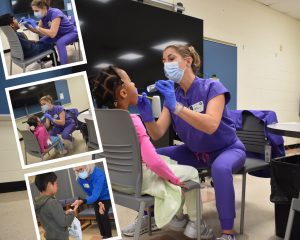
DPH Oral Health Screening Programs Support Students’ Healthy Smiles and Expand Access to Dental Care
Date Posted: October 29, 2024

Opioid Fund Co-Chairs Release Roadmap to Recalibrate Use of Settlement Funds
Date Posted: October 28, 2024

New HSCA Rate Goes into Effect in January
Date Posted: October 28, 2024

AG Jennings resuspends financial advisor for illegally accessing former clients’ account information
Date Posted: October 28, 2024

DOJ secures more than two decades of prison time in cold case murder
Date Posted: October 28, 2024

Housing Assistance Applicants Should Update Information On Public Housing Waitlists By Nov. 22
Date Posted: October 28, 2024

Delaware Forest Service Opens Grants for Local Communities
Date Posted: October 28, 2024

Office of the Marijuana Commissioner (OMC) Conducts Lottery for Delaware’s Regulated Marijuana Industry
Date Posted: October 25, 2024

Governor Carney, with Guidance from Water Supply Coordinating Council, Declares Statewide Drought Watch
Date Posted: October 25, 2024

Tag-A-Palooza 2024
Date Posted: October 24, 2024

Office of the Marijuana Commissioner: Licensing Lottery
Date Posted: October 23, 2024

AG Jennings issues open letter to Delaware landlords urging Delaware Landlord/Tenant Code Compliance
Date Posted: October 22, 2024

New Housing Vouchers for Delaware Families
Date Posted: October 21, 2024

Piping Plover Population in Delaware Experiences Slight Decline, Offset by Higher Nesting Success
Date Posted: October 21, 2024

National Slow Down Move Over Day Observed as Delaware Sees Near Record Crashes
Date Posted: October 18, 2024

Delaware Officials Unveil New Sign to Celebrate Delaware’s Agricultural Lands Preservation Program
Date Posted: October 17, 2024

DOJ secures prison time for former trooper
Date Posted: October 16, 2024

Colonial Teacher Named Delaware 2025 Teacher of the Year
Date Posted: October 15, 2024

Governor Carney Orders Lowering of Flags
Date Posted: October 15, 2024

Delaware Faces Dry Conditions: Open Burning Ban Issued, Water Conservation Urged
Date Posted: October 15, 2024

Burning Ban
Date Posted: October 15, 2024

DelDOT Announces 4th Annual Name That Plow Contest
Date Posted: October 15, 2024















































































